Defect-Mediated Cu–S Pair Active Sites Modulating Proton Supply to Facilitate Overall CO2 Photoreduction with H2O
Release time:2024-07-09
Hits:
- DOI number:
- 10.1021/acscatal.4c02857
- Journal:
- ACS Catalysis
- Abstract:
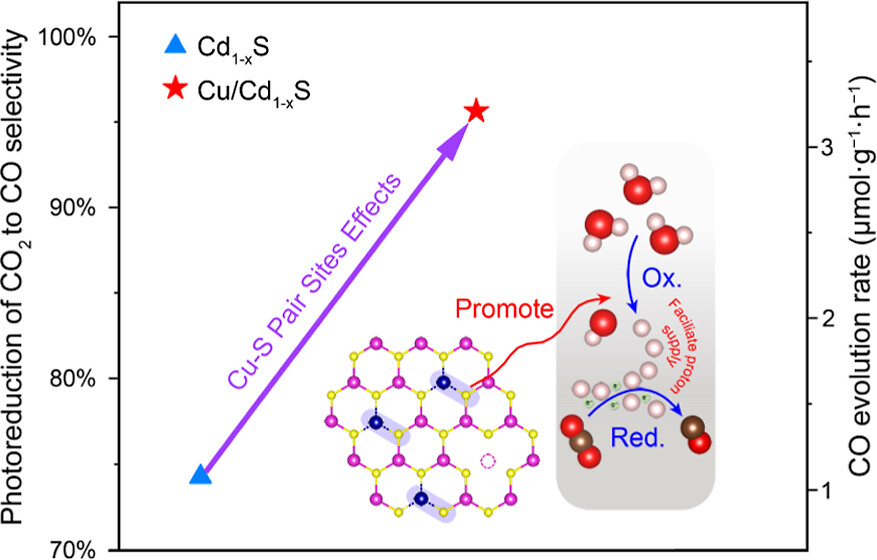
- Precise design of photocatalysts with the demanded active surface structure for highly efficient and selective CO2 photoreduction is crucial but challenging. Here, by taking CdS as a prototype, single-atom Cu is successfully constructed on Cd-deficient CdS (Cd1–xS) to improve the performance of CO2 photoreduction with H2O as proton donor. The optimal Cu/Cd1–xS with Cd vacancies (VCd)-mediated single-atom Cu exhibits nearly 100% selective CO production and a more than three-fold higher CO evolution rate compared to that of Cd1–xS. Both experimental identification and DFT theoretical simulation unveil that the VCd-mediated single-atom Cu render Cu–S pair sites to function as more catalytically active sites for dissociating H2O and promoting the corresponding proton supply, which favors the subsequent protonation of the adsorbed CO2 at the adjacent Cd sites via the two-proton coupled two-electron transfer pathway. This work demonstrates the importance of modulating proton supply from the oxidation half-reaction for facilitating the overall CO2 photoreduction, advocating an overall-reaction perspective for the design and development of highly efficient and selective CO2 conversion photocatalysts.
- Volume:
- 14
- Issue:
- 13
- Page Number:
- 9734-9741
- Translation or Not:
- no
- Date of Publication:
- 2024-06-14


